Application Rationalization
The strategic process of evaluating and optimizing an organization's portfolio of applications to make informed decisions about their placement, modernization, or retirement in the cloud environment. The goal is to align the application portfolio with business objectives, enhance operational efficiency, and maximize the benefits of cloud computing.
Application rationalization is a critical step in a cloud migration strategy, helping organizations optimize their IT landscape for efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and agility. It enables informed decision-making, ensuring that the selected applications contribute positively to the overall cloud adoption goals and deliver maximum value to the organization.
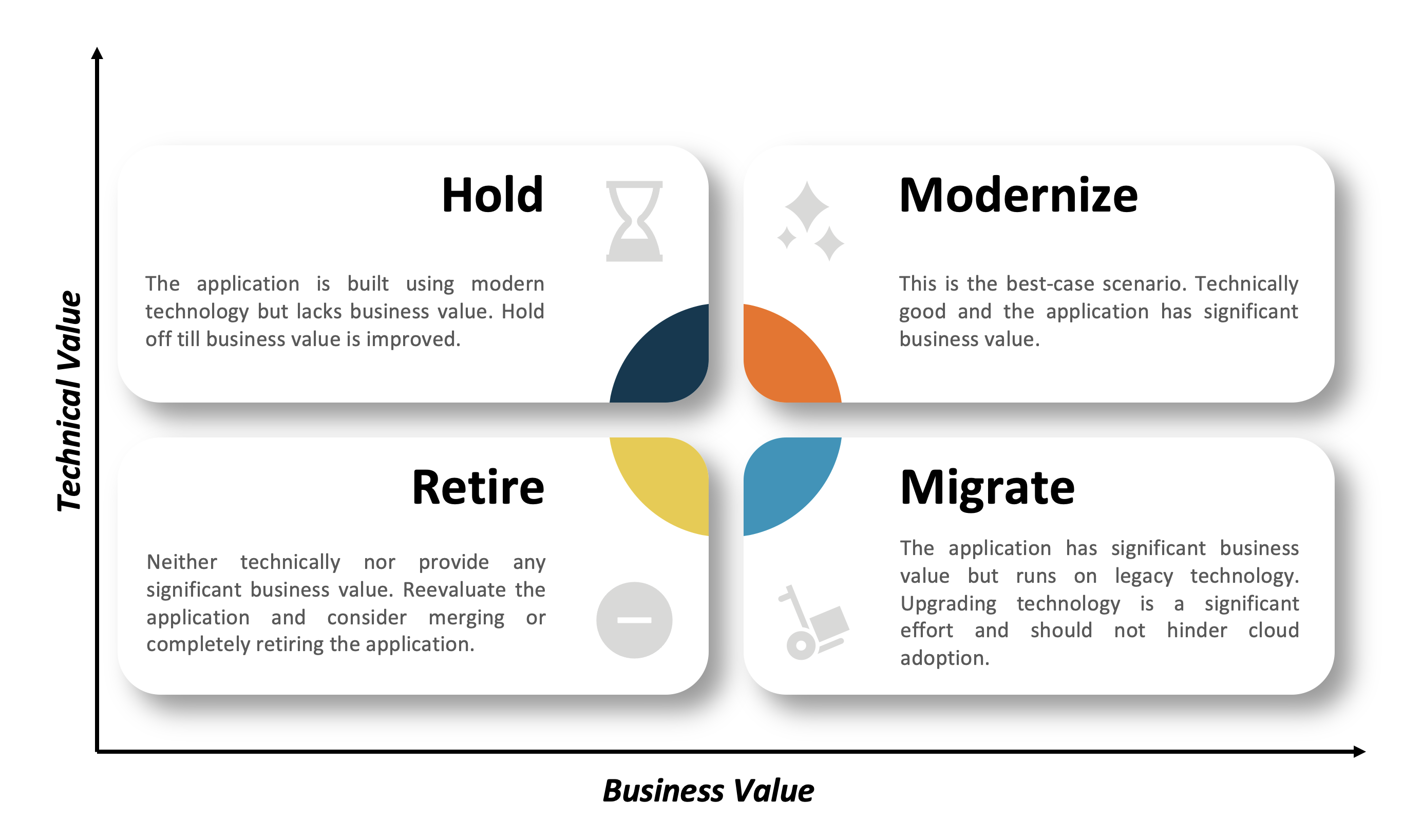
Application Assessment
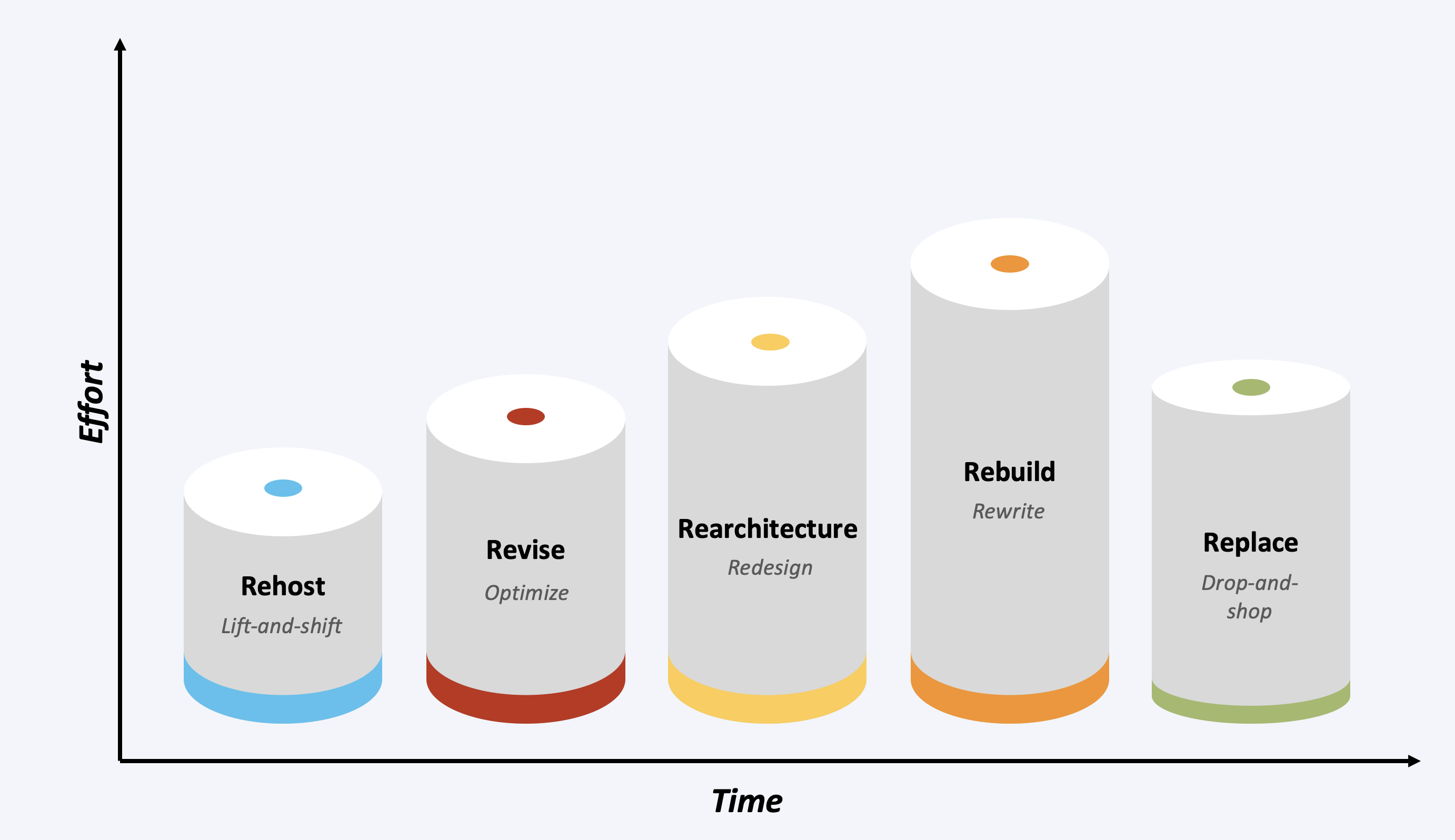
Application assessment involves a careful analysis of each application's architecture, dependencies, and requirements. Use 5 R's principles of Rehost, Revise, Rearchitect, Rebuild, and Replace to determine the strategy for cloud migration.
- Rehost (Lift and Shift) - move applications to the cloud without making significant changes
- Revise (Optimize) - minor optimization to application design and functionality without undergoing a complete overhaul.
- Rearchitect (Redesign) - significant changes to the application architecture to leverage cloud services fully
- Rebuild (Rewrite) - rewrite the application from scratch to take full advantage of cloud-native services and features
- Replace (Drop and Shop) - discard the existing application and adopt a commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) or SaaS solution
Cloud Migration
Application migration to the cloud involves the transfer of an existing application from on-premises or another environment to a cloud computing platform. This migration primarily focuses on relocating application components, including code, data, and configurations, to the chosen cloud infrastructure.
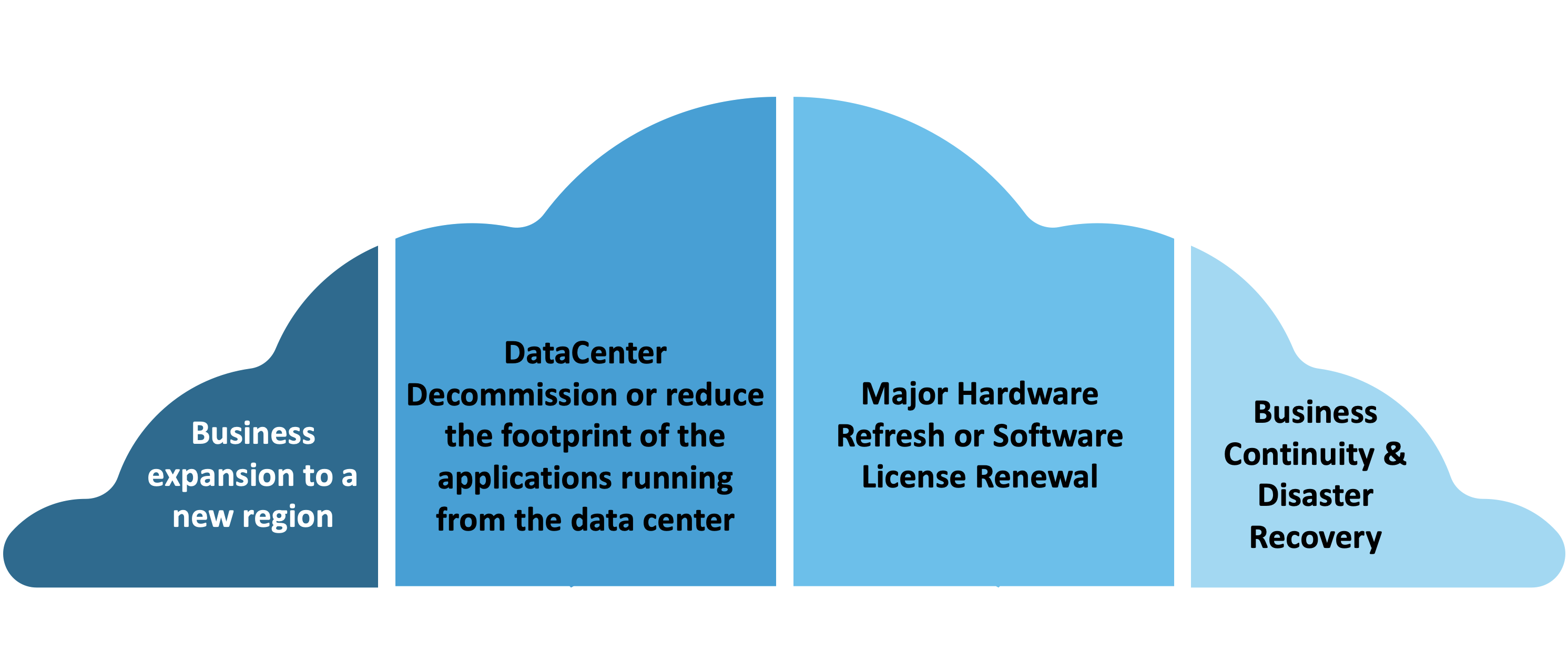
The major reasons we see organizations migrating to cloud are:
- Business expanision - The cost and efforts of owning/renting, managing, and meeting the regulatory compliance for a data center is much higher than adopting the cloud
- Datacenter decommission - To reduce operational overhead and capital expenses
- Major hardware refresh - The cost to replace obsolete hardware is much higher than renting the infrastructure on the cloud
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery - Set up the cloud environment with minimal cost and use it only in the event of disruptions.
Cloud Modernization
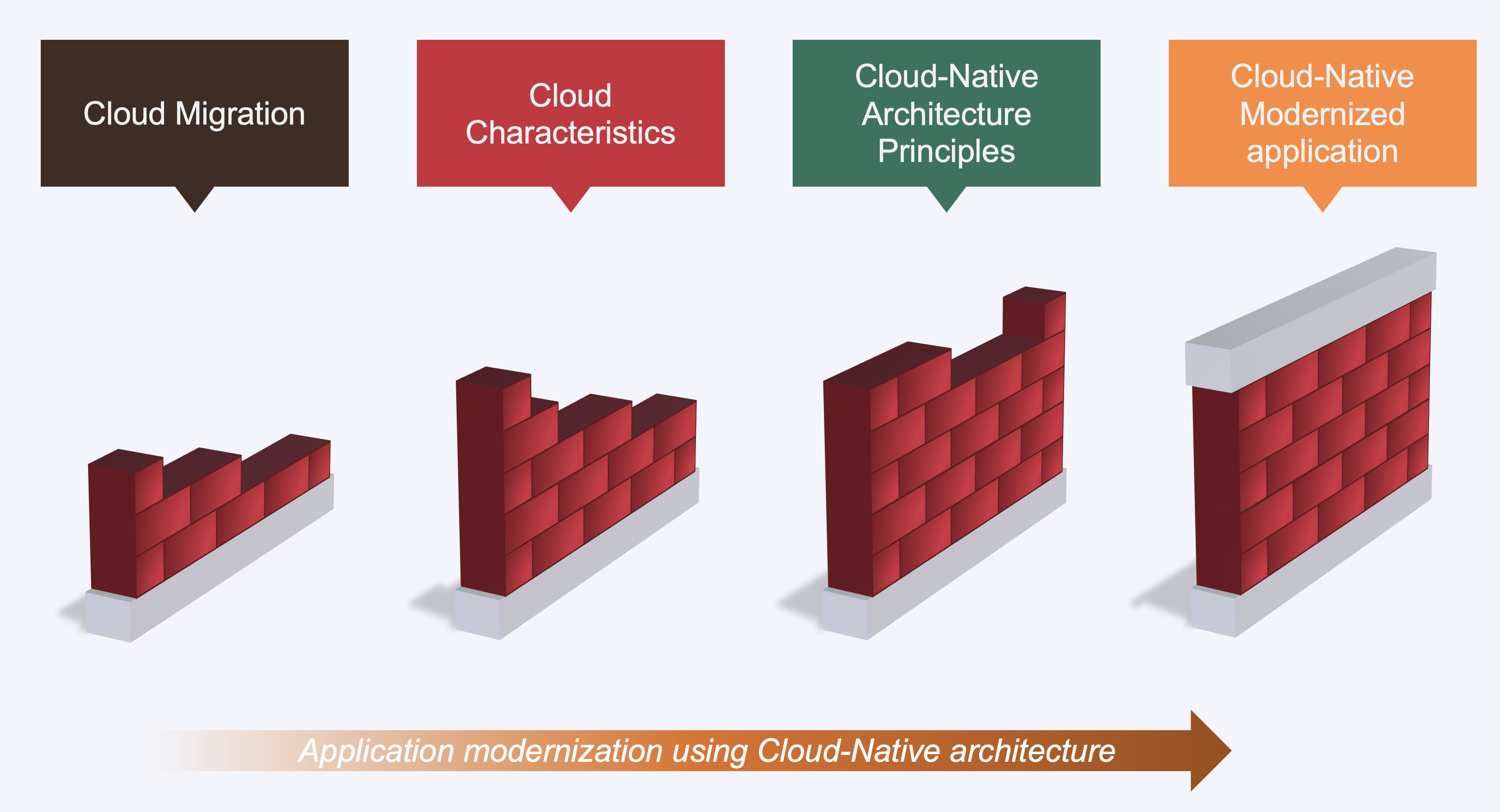
Cloud modernization involves restructuring, refactoring, rearchitecting, or rewriting application components to align with cloud principles such as scalability, microservices, serverless computing, and containerization.
When organizations migrate their applications to the cloud, they often have high expectations for the benefits they will receive. However, the results often fall short of these expectations. To truly take advantage of all the benefits of the cloud, it is important to modernize the application. This means rearchitecting or rebuilding it to utilize the unique characteristics of the cloud and incorporate cloud-native architecture principles. By doing so, organizations can achieve the full potential of their cloud migration and reap the benefits of increased efficiency, agility, and scalability.
